Benyahlou Zohra Douaa1, Yahiaoui Salem2, Belhachemi Mohammed Hadj Mortada1, Abdelkader Chouaih1
1Laboratory of Technology and Solid Properties (LTPS), Faculty of Sciences and Technology, Abdelhamid Ibn Badis University of Mostaganem, 27000 Mostaganem, Algeria
2Ecole Normale Supérieure de Mostaganem, 27000 Mostaganem, Algeria
benyahlou.zohra.douaa@gmail.com
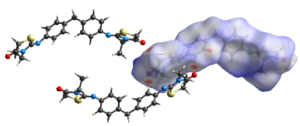
The current study focuses first on the synthesis of a new organic heterocyclic compound. The (Z) 4,4′-bis[-3-N-ethyl-2-N’-(phenylimino) thiazolidin-4-one] methane (2-EPTh) was synthesized for the first time and its structural characterization was performed by single crystal X-ray diffraction (XRD). Crystallographic data revealed that the compound crystallizes in the P-1 space group of the triclinic system with two independent molecules in the asymmetric unit. According to the values of the dihedral angles, the structure was found to be significantly non-planar. To support and rationalize the experimental results, density functional theory (DFT) calculations have been performed using the B3LYP and CAM-B3LYP functionals with 6-311G (d,p) basis set. Results of optimized geometry are almost identical to the experimental results. Furthermore, to ensure the contribution of intermolecular interactions, Hirshfeld surface analysis and 2D fingerprint plots were performed. The corresponding results show that H∙∙∙H (49.1%) and H∙∙∙C/C∙∙∙H (19.6%) are the main contributors to the intermolecular interactions, which stabilize the crystalline structure. Strong and weak van der Waals repulsive and attractive interactions were studied by RDG analysis, and the energies associated with intermolecular interactions and their nature were calculated. Finally, molecular docking study was realized to understand the structure-activity relation.
Keywords: heterocycle; XRD; H-bonds; bond energy; docking
